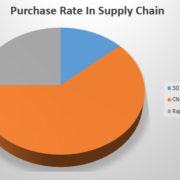
In Regard To Material Selection in Prototyping Industry
When choosing materials for prototyping, you should first consider which features are most important for your end user. You may feel like you don’t have to make a compromise on any feature, but you might end up with a product that is too heavy or too cheap. You may have to compromise on certain features for durability. Nevertheless, choosing the right material will help you minimize costs, reduce delays, and ensure your customers have a positive experience with your product.
When choosing the material, it is vital to know the properties of the material. it is essential to consider the end product’s shape and size. A dense material can make the product heavy. If it is too fragile, the weight of the product may cause problems for users. A lightweight material may be sufficient for an end user, but a heavier one will not be durable. In order to make the final product, consider the size and components of the end user.
The Diversity of Prototyping Material
Foam core, a flat prototyping material, is widely available in retail stores and is inexpensive. It can be carved into 3D shapes and is useful for form models and ergonomic studies. It can also be used as a tool for fast prototyping. It is useful in a variety of applications, from rapid product development to detailed research. For more information, read Lichter and Lowgren (2009). The following is a short list of pros and cons of foam core.
Polyoxymethylene, a hard plastic with immense wear resistance, is widely used in gears and bearings. It is also used for making machine tools, instruments, toys, and auto parts. Another common plastic used for rapid prototyping is Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, which is affordable and easy to use. Both Polyoxymethylene and ABS are popular alternatives to plastic. These materials offer a variety of advantages, including ease of use and affordability.
-
Plastic Material
Polyoxymethylene, for example, is a hard plastic with tremendous wear resistance. It is used to make gears, bearings, and other automotive components, and is also used in industrial equipment and toys. Its low weight density and relative affordability make it an appealing choice for rapid prototyping. However, this material is not cheap; it is not a sustainable option, and is not yet a sustainable material. Regardless of its high cost, its use is growing.
Despite the high price, the advantages of rapid prototyping make it a valuable investment. The material’s high machinability coefficient makes it an excellent material for prototypes. This is important because ABS plastics can warp if not chosen carefully. But ABS is a great choice for 3D printing, thanks to its low cost and high strength. If you’re looking for a material to use for a 3D printer, ABS is the best choice for the job.
-
Metals Material
There are many metal materials used for rapid prototyping are aluminum, titanium, brass, and steel. Aluminum is the most common, but steel is also an excellent option. The two metals steel and aluminum are relatively inexpensive and can be recycled if the model does not wear out. Aluminum, however, is a better option. In addition, it is also durable and strong, but it can be inexpensive. Its weight can also hinder the creation of new designs. Many numbers for your choose , such as 6061.6063.7075…etc. It is the most widely metal in the world.
-
ABS: The most common plastic
In the past, ABS was used in rapid prototyping, which is a process that requires precise measurements and accurate information. It can be used to test and improve final products. It is not suitable for mass production. In addition, it cannot be reused. It is important to choose the right material for your project. If you need to use a metal for your model, make sure it has a low weight. The wrong type of material can affect manufacturing.
Various types of material are used for rapid prototyping. Some materials are better suited for some applications than others. The material used will depend on the requirements of the project and its application. Generally, materials are used for prototypes that have low cost and high production volume. But the most common materials are ABS, polypropylene, nylon, and urethane. In some cases, plastic may be too expensive or not durable enough for the application.
Material Selection in Prototyping
The process of material selection in prototyping is an integral part of product development. It is important to choose the right material for the right application, which will determine the performance characteristics of the finished product. The article also examines the performance characteristics of different materials, highlighting the factors that influence the selection of a specific type of material. Some of these factors include the design, process, and volume of the final product, as well as the need for materials data and information.
Choosing materials for prototyping is a critical component of product creation. Materials should be durable for the intended use cases, as well as affordable for the end consumer. Depending on the type of product and the intended market, the right material can save time and money. While choosing materials for prototypes is a crucial step, it is important to remember that the right material will ultimately affect the end result. It will also help you ensure that your product meets the desired functionality and quality.
When choosing materials for prototyping, it is important to remember that not all materials are equal. Some are more durable than others, and you may want to compromise on some of them. When it comes to product design, it is important to consider what features your end users will value the most. Premium materials are not inexpensive, but they will save you money in the long run. Considering the costs of materials is crucial for successful prototyping.
The Bottom Line
Choosing materials wisely is crucial to a successful product development. Choosing the right material for the job is essential for the production of prototypes. It is important to consider the cost, durability, and weight requirements of the product. Similarly, the material should not be too expensive or too dense. It is important to consider the cost, weight, and size of the end product before deciding on the material to be used.